The End of the “Traditional Students” as We Know Them
Demographics show that our society will become more diverse. Students in the future will not only be more diverse by nature, but also by situation. This might mean they have to balance work and family with education or that they have previously disengaged with a college.
Over the past decade, colleges and universities struggled, yet the warning bells went largely unheeded. The National Student Clearinghouse (NSC) shows that higher education lost 2.7 million participants between 2010 and 2020. While some of this can be attributed to the recent effects of the pandemic and the declining number of college-aged students, other factors and causes are at play such as rising tuition, concern regarding job placement, perceived lower return on investment and less favorable household finances.
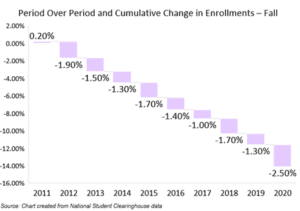
Higher education needs to work harder for every enrollment … and not just the traditional 18 to 22 year-old college student. They need to reverse a troubling downward trend that is being compounded by employers taking more control and responsibility for training their own workforce and becoming less dependent on higher education to do so.
Every enrollment must be fought for to make up for these losses and the previously ignored or under-valued potential students include:
The Adult or Part-Time Learner or Transfer Student: Of the 18 million students enrolled during the Fall of 2020 [i], just over one third were part-time learners. A similar percentage and number of part-time learners were enrolled during the Spring of 2021 [ii]. Higher education institutions need to market to and engage these credit-carrying students differently from the 18 to 22 year-old learner. This group has different motivations and goals. In 2021, UPCEA and Thinking Cap Agency recently completed a study of the many faces of the adult or part-time learner [iii]. Programs will have to be more accessible, stackable, flexible and relevant to attract these learners.
The Disengaged Learner: The pandemic drove many students from the classroom to the sidelines. Many of these former students question the quality of the education they are receiving, as well as whether or not it will adequately prepare them for a new and more automated economy. In 2021, UPCEA and StraighterLine conducted an analysis [iv] of disengaged learners and found that they leave college for many reasons. The report also identifies opportunities for higher education to reconnect and engage these otherwise lost learners. No longer can colleges and universities treat these students as “not good enough” for their institution. Institutions are going to need a quicker and better response when students disengage and genuinely invite them back to the institution, but through different channels and with greater support. Degree-completion and stackable credentials could also make a degree a more reachable goal for this learner.
Young Men: While young women look at higher education as a means to achieve equitable pay with men, the National Student Clearinghouse and the New York Times [v] identified that men view education very differently. Young men are less confident about whether or not the investment in time and money will yield a strong salary and high likelihood of employment in a future economy that may be evolving at a faster pace than higher education. Higher education will need to rethink its curriculum and communications to attract and retain young men in the future. If they continue to disengage with higher education in favor of immediate higher paying vocational jobs, then professional, continuing and online education units may have an opportunity in the near future. Young men may see more value in a curriculum that is stackable that gives them micro-credentials along the way. These learners, like their young Millennial (those aged 26 to 30) cousins, seek smaller rewards with more frequency, and badges and certificates that can be applied in stackable and noncredit-to-credit transfer modalities are likely to be more attractive.
Your Own Alumni: Colleges and universities need to rid themselves of legacy thinking when it comes to alumni. In many conversations with PCO leaders, access to alumni is either extremely limited or unavailable for marketing for continuing and professional education. Generation Z (those age 25 and younger) and younger Millennials have strong brand preferences. However, college and university alumni and development officers prevent PCOs access to alumni to preserve them for capital campaigns and fundraising efforts. The legacy thinking of alumni as willing contributors fades with younger alumni who desire a stronger and more meaningful relationship, one where continuing education could play a role. A recent UPCEA snap poll of 48 institutions shows that just one-in-four PCO units are programmatically engaged with alumni. Just over one-in-three have access to market to alumni. In my research for specific colleges and universities, alumni want more engagement with the institution besides being constantly solicited for donations and contributions only. 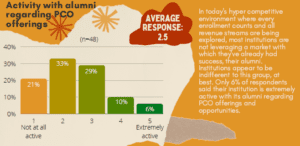
The High School Graduate: While this audience may appear to be adequately addressed through traditional efforts by the institution, the pandemic has changed the value equation for many segments of high school graduates. Through online learning, some graduates may seek less traditional educational opportunities as they may look for greater value. This value-seeking or cost-sensitive student may have previously sought out educational providers in a limited geographic region, wanting less expensive opportunities where they could commute and avoid residential or student fees. However, the pandemic created more opportunities and providers for these students. Another high school segment might not be value or cost-sensitive, but may prefer the comforts of home and family they have become more dependent on during the pandemic. Many high school and elementary students were negatively impacted [vi] from accessing quality education during the pandemic, especially people of color [vii]. More on-ramps to higher education need to be established to serve these students as well, as many struggled with access to technology and other services needed for a quality, preparatory education to college.
The Skill Builder: Many institutions offer professional education and training … and many do not. Some institutions also place a lesser value on noncredit education. It is very likely that noncredit education will play a much larger and more important role in the future of higher education as badges and alternative credentials gain traction. Should noncredit-to-credit transfer and badging become more prevalent at leading mainstream institutions, we will likely see more programs developed to develop skills and specializations.
The Incarcerated or Formerly Incarcerated: The U.S. leads the world with the number of individuals behind bars. As of March 2021, there were 1.8 million individuals incarcerated [viii]. In 2022, the Second Chance Pell Program [ix] will be expanded to help the incarcerated access free or subsidized education while in prison. While providing access to education to the incarcerated is well within the mission/vision of many institutions, few are doing so [x] despite the well-researched societal benefits. Research shows that individuals who had earned their degree while incarcerated show an increase in earnings and number of hours worked, as well as a decrease in recidivism [xi].
To compete in the future, institutions are going to need to go beyond the degree, as demographics become less favorable and competition in the form of “substitute” educational products offered by private providers is likely to grow. Institutions will have to offer educational products and programs that are designed with the needs of the new adult learner and employer in mind.
In addition to designing programs around the learner and employer, marketing and communications will need to be developed and implemented to support the programs. This includes not only strategic messaging, but also user-centered website development and social media. Enrollment management strategies will have to be implemented to convert inquiries to applicants and applicants to enrollments and retention tactics put in place to prevent disengagement.
If the industry or collective institutions of higher education can effectively address these audiences above, they can redefine the role that colleges and universities play over the next decade. The higher education industry can become more relevant and connected to the economy and its citizens, and change the course of what otherwise would be an unfortunate future for so many institutions.
If this is to happen, there will be no place for the word “traditional” in the future of higher education.
[i] https://nscresearchcenter.org/wp-content/uploads/CTEE_Report_Fall_2020.pdf
[ii] https://nscresearchcenter.org/wp-content/uploads/CTEE_Report_Spring_2021.pdf
[iii] https://www.thinkingcapagency.com/whitepaper-new-learners/
[iv] https://upcea.edu/new-research-answers-question-every-college-wants-to-know-why-do-students-leave-and-how-do-we-get-them-back/
[v] https://www.nytimes.com/2021/09/09/upshot/college-admissions-men.html
[vi] https://www.nwea.org/content/uploads/2021/06/Understanding-the-initial-educational-impacts-of-COVID19-on-communities-of-color.Resear-hBrief.pdf
[vii] https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/27/us/covid-race-impact-black-education.html
[viii] https://www.vera.org/downloads/publications/people-in-jail-and-prison-in-spring-2021.pdf
[ix] https://www.ed.gov/news/press-releases/us-department-education-announces-it-will-expand-second-chance-pell-experiment-2022-2023-award-year
[x] https://irle.berkeley.edu/benefits-of-higher-education-for-formerly-incarcerated-people/
[xi] https://www.vera.org/downloads/publications/investing-in-futures.pdf
Learn more about UPCEA's expert consultants.
Do you need help with your PCO unit or campus? We can help. Contact UPCEA Research and Consulting for a brief consult. Email [email protected] or call us at 202-659-3130.
Trusted by the nation's top colleges and universities, UPCEA Research and Consulting provides the best value in the industry today. UPCEA's industry experts have years of experience in Online and Professional Continuing education - put them to work for you!
UPCEA Research and Consulting offers a variety of custom research and consulting options through an outcomes-focused pricing model. Find the option(s) that best suit your institution.
Learn more about UPCEA Research & Consulting
The UPCEA Difference
Unmatched Experience: For more than 100 years, UPCEA consultants have exclusively served the needs of online and professional continuing education programs. UPCEA consultants leverage their extensive industry expertise to expedite solutions, anticipate upcoming shifts, and offer distinct best practices, effectively aiding clients in achieving their goals.
Cost Effectiveness: As a nonprofit, member-serving organization, we provide unmatched value, allowing you to maximize limited research and consulting budgets.
Action in Motion: Our cadre of experienced, skilled authorities and expert practitioners propels you forward, translating research and consulting into impactful implementation, a distinctive hallmark of UPCEA. Our team of current and former institutional leaders will support you, turning research and consulting into action.
Mission Alignment: Like you, our mission is to enhance and expand educational opportunities and outcomes for adult and other non-traditional learners. We share your values and work in partnership with you to advance access and excellence in education.
